Conditions
Neuroinflammation Symptoms Explained by Expert Neurologist: Discover Root Causes and Create an Action Plan for a Healthier Brain
Published: September 14, 2024
Author: Dr. Achillefs Ntranos MD

Could Neuroinflammation Be Causing Your Symptoms?
You've been dealing with persistent brain fog, unexplained fatigue, cognitive difficulties, or memory issues that just won't go away. Maybe you've seen multiple doctors, tried different approaches, and still don't have answers. Now you're wondering: could brain inflammation or neuroinflammation be the missing piece?
Neuroinflammation — an inflammatory response within the brain and spinal cord — is more than a medical buzzword. It is a complex process that can contribute to a wide range of symptoms, from persistent brain fog, fatigue, and mood swings to more severe cognitive or autonomic dysfunction. However, it's rarely a diagnosis on its own — it typically points to an underlying root cause that can often be identified and addressed with the right treatment.
In this comprehensive guide, we'll break down the causes, symptoms, diagnostic steps, and available treatments for neuroinflammation. We'll also discuss actionable lifestyle measures you can implement to optimize brain health, reduce brain inflammation, and improve your quality of life.
Understanding neuroinflammation can help you recognize when to see a neurologist for evaluation and guide you toward effective, tailored treatments.
What is Neuroinflammation?
Think of neuroinflammation like a fire alarm system in your brain. When functioning properly, it helps protect and repair neural tissue after injury or infection. But when this system stays activated too long or becomes triggered inappropriately, it can cause damage rather than healing.
When your brain is inflamed:
- Communication between brain cells becomes disrupted
- Essential nutrients and oxygen may not be properly used by cells
- Waste removal systems become less efficient
- Brain circuits responsible for memory, mood, and energy regulation can malfunction
Silent Symptoms
Many people don't realize they're experiencing neuroinflammation. It often presents as subtle changes in thinking, energy levels, or mood rather than pain or obvious physical symptoms.
Symptoms of Neuroinflammation
When neuroinflammation gets out of control and becomes persistent, it can cause a range of symptoms, influenced by the underlying cause and the specific brain regions involved:
- Cognitive Difficulties: Persistent brain fog, forgetfulness, difficulty focusing, and slowed information processing. These cognitive and memory symptoms can significantly impact daily functioning.
- Mood Changes: Increased anxiety, depression, irritability, or mood swings without an identifiable psychological trigger.
- Sleep Disturbances: Persistent tiredness, difficulty falling or staying asleep, and unrefreshing rest.
- Headaches & Dizziness: Chronic headaches or bouts of vertigo that don't resolve with common measures. In Southern California, environmental migraine triggers can worsen neuroinflammation and contribute to persistent headache symptoms.
- Autonomic Dysfunction: Irregularities in blood pressure, heart rate, digestion, or temperature regulation may indicate inflammatory impacts on the autonomic nervous system.
- Chronic Fatigue Syndrome/ME: Characterized by profound fatigue, cognitive dysfunction, and post-exertional tiredness.
When to Seek Medical Advice
If you're experiencing persistent cognitive symptoms, unexplained fatigue, or mood changes that interfere with daily life, don't dismiss these as "just stress" or "getting older." These could be signs of neuroinflammation that deserve proper evaluation and treatment.
The Spectrum Of Neuroinflammation
Neuroinflammation is not a binary condition. It exists on a spectrum from beneficial to harmful. While excessive inflammation damages the brain, controlled inflammatory signals support learning, neural development and tissue repair, as well as protect against infection. Understanding this balance explains why completely suppressing inflammation can be detrimental.
| Aspect | Beneficial inflammation | Harmful inflammation |
|---|---|---|
| When it happens | Mild, short-term | Severe or long-term |
| What it does | Boosts brain communication, helps memory and learning, repairs tissue, protects the brain, builds resilience to stress | Causes brain injury, leads to anxiety and depression, weakens memory and learning, accelerates aging, triggers neurodegenerative diseases |
| Examples | Minor immune alerts, recovery after small injuries, training the brain to handle stress | Traumatic brain injuries (TBI), chronic stress, aging-related inflammation, diseases like Alzheimer's and Multiple Sclerosis |
| Key molecules involved | IL-1 (supports communication), IL-4 (healing and protection) | IL-1, IL-6, TNF, IFNγ (cause inflammation), ROS, iNOS (damage brain cells) |
| Overall impact | Healing and protection | Damage and disease |
Key Players in Neuroinflammation: Orchestrating a Delicate Balance
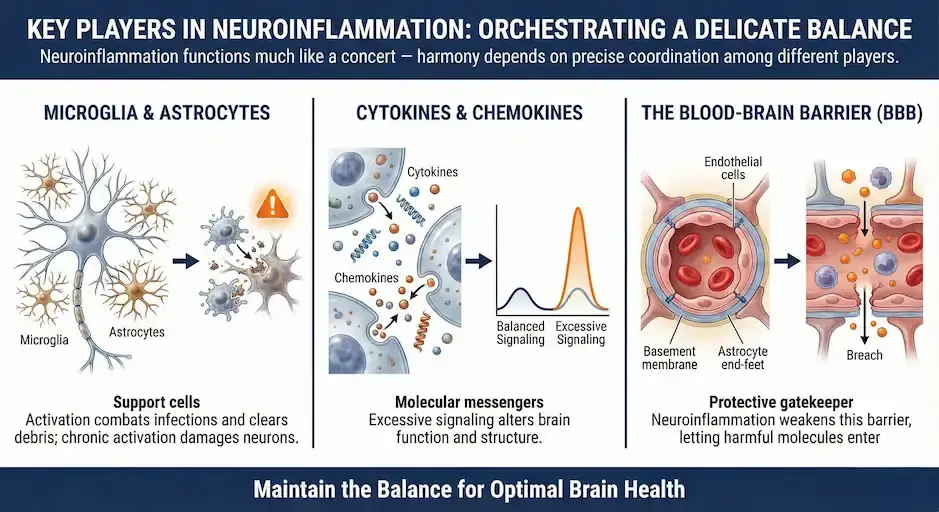
Neuroinflammation functions much like a concert — harmony depends on precise coordination among different players:
- Microglia & Astrocytes: Support cells in the CNS, essential for maintaining brain health. Activation allows them to combat infections and clear debris, but chronic activation can damage neurons.
- Cytokines & Chemokines: Molecular messengers regulating inflammation; excessive signaling can alter brain function and structure.
- The Blood-Brain Barrier (BBB): A protective gatekeeper controlling substance entry into the brain. Neuroinflammation can weaken this barrier, letting harmful molecules enter and amplify inflammation.
Microglia: Your Brain's Immune Guards
Microglia are your brain's resident immune cells and play a central role in neuroinflammation. These specialized cells:
- Act as first responders to injury, infection, or stress
- Constantly scan your brain for threats using their branch-like extensions
- Release protective or damaging compounds depending on the situation
- Can become "primed" by previous challenges, making them more reactive to future stressors
- Function in both protective and potentially harmful ways depending on their activation state
The balance between different microglial states significantly influences whether inflammation helps or harms your brain.
What Triggers Neuroinflammation?
Different conditions, environmental factors, and lifestyle choices can cause harmful brain inflammation:
| Trigger | How It Causes Inflammation |
|---|---|
| Head Injuries | Even mild concussions can activate inflammatory pathways that sometimes persist long after the initial injury. |
| Infections | Viruses (including COVID-19) or bacteria (like Lyme disease) can trigger persistent inflammation in the brain after the infection has cleared. |
| Autoimmune Conditions | In diseases like Multiple Sclerosis, your immune system mistakenly attacks brain tissue, creating ongoing inflammation. |
| Sleep Disturbances | Poor sleep, sleep deprivation, and sleep disorders, such as sleep apnea, can amplify and prolong inflammatory responses in your brain. |
| Chronic Stress | Persistently elevated stress hormones can sensitize inflammatory cells in the brain, creating a cycle of inflammation and stress. |
| Your Gut Health | The gut and brain communicate constantly. An unhealthy gut microbiome can send inflammatory signals to your brain via the gut-brain axis. |
| Environmental Toxins | Toxins, pollutants, and certain foods can cross the protective blood-brain barrier and trigger inflammatory responses. |
| Toxic Metals | Heavy metals like lead, mercury, and aluminum can cause neuroinflammation. |
| Chemotherapy | Certain chemotherapies can cause neuroinflammation as a side effect, resulting in "chemo brain", a condition affecting memory and concentration issues. |
How We Diagnose Brain Inflammation
Uncovering neuroinflammation often requires a comprehensive and individualized approach:
- Your Story Matters: A detailed review of your symptoms, timeline, exposures, and medical history provides crucial clues
- Neurological Examination: A thorough physical examination can identify signs of inflammation or neurological damage
- Laboratory Testing: Blood tests can reveal inflammatory markers, autoimmune antibodies, or signs of infection
- Brain Imaging: Advanced MRI techniques can show subtle changes in brain structure or function related to inflammation
- Neurophysiological Testing: EEG, nerve conduction studies, or autonomic testing can highlight functional disturbances tied to inflammation.
- Spinal Fluid Analysis: A lumbar puncture may identify inflammatory proteins or immune cells present in your central nervous system
- Cognitive Assessment: Neuropsychological testing can map specific cognitive patterns affected by inflammation
- Sleep Study: Home Sleep Apnea Testing can quickly identify sleep apnea, which can affect the brain and cause neuroinflammation.
What Are The Treatments for Neuroinflammation?
The best way to reduce neuroinflammation is to not only address the underlying causes but also support your brain's natural healing processes:
Medical Interventions
Anti-inflammatory Medications: From targeted biologics to corticosteroids, medications can help calm an overactive immune response
Immunomodulatory Therapies: For autoimmune-driven inflammation, disease-modifying therapies adjust the immune system activity to prevent further damage
Cognitive Rehabilitation: Memory exercises, occupational or speech therapy, and structured cognitive training can help restore or maintain cognitive functions.
Symptom Management: Medications or therapies to address specific symptoms, such as autonomic dysfunction, headaches, or sleep disturbances.
Lifestyle Changes to Calm Neuroinflammation and Promote Brain Health
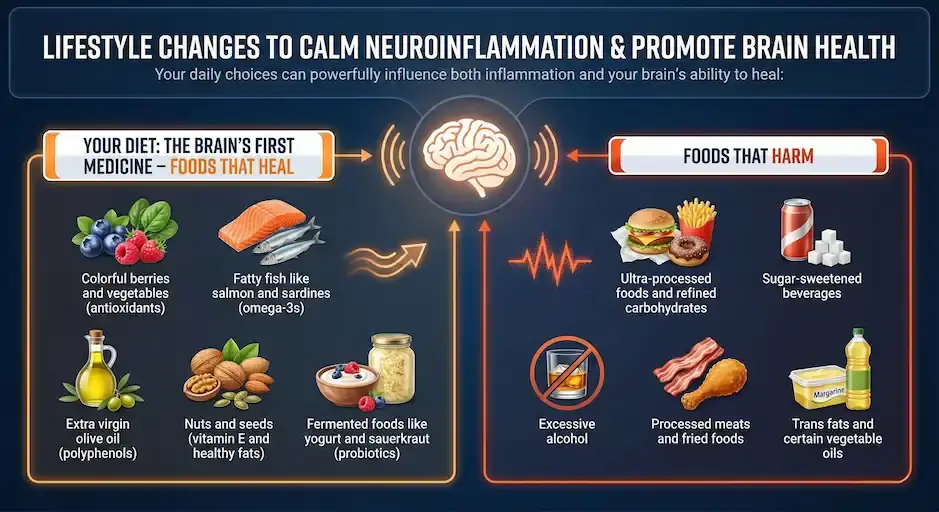
Your daily choices can powerfully influence both inflammation and your brain's ability to heal:
Your Diet: The Brain's First Medicine
Foods That Heal:
- Colorful berries and vegetables (antioxidants)
- Fatty fish like salmon and sardines (omega-3s)
- Extra virgin olive oil (polyphenols)
- Nuts and seeds (vitamin E and healthy fats)
- Fermented foods like yogurt and sauerkraut (probiotics)
Foods That Harm:
- Ultra-processed foods and refined carbohydrates
- Sugar-sweetened beverages
- Excessive alcohol
- Processed meats and fried foods
- Trans fats and certain vegetable oils
Movement as Medicine: Regular, moderate exercise reduces inflammatory markers, improves blood flow to the brain, and enhances neuroplasticity
Hydration is Key: Drinking enough water is essential for brain health as it helps with toxin elimination through the kidneys and maintains cerebral blood flow. Dehydration can lead to brain fog and other symptoms.
Sleep Quality: Your brain's cleaning and repair systems activate during sleep. Addressing sleep issues or treating sleep apnea is crucial for reducing neuroinflammation
Stress Management: Chronic stress fuels inflammation. Practices like meditation, mindfulness, and other relaxation techniques can break this cycle. For more persistent stress and anxiety, consider therapies like cognitive-behavioral therapy or biofeedback.
Social Engagement: Social connections create positive neurochemical changes that support brain health.
Neuroplasticity: Your Brain's Recovery Mechanism
Neuroplasticity is your brain's remarkable ability to reorganize itself by forming new neural connections throughout life. In the context of neuroinflammation, it becomes crucial for recovery - as inflammation subsides, neuroplasticity enables your brain to rebuild damaged circuits, create alternative pathways around affected areas, and restore function.
The lifestyle factors mentioned above (anti-inflammatory diet, exercise, quality sleep) don't just reduce inflammation; they actively support neuroplasticity, enhancing your brain's natural healing capabilities. This is why comprehensive treatment approaches often yield better results than simply targeting inflammation alone.
Your Action Plan for a Healthier Brain
| Daily Practice | Why It Matters |
|---|---|
| Eat Anti-Inflammatory Foods | Provides building blocks for brain repair and reduces inflammatory signals |
| Move Your Body | Enhances neuroplasticity and stimulates anti-inflammatory pathways |
| Stay Hydrated | Supports toxin elimination through the kidneys and maintains cerebral blood flow |
| Prioritize Sleep | Activates the brain's cleaning system and cellular repair mechanisms |
| Manage Stress | Reduces cortisol and other inflammatory triggers |
| Connect Socially | Social engagement creates positive neurochemical changes that support brain health |
When to Reach Out for Help
Contact our clinic if you experience:
- Persistent cognitive difficulties affecting work or daily activities
- Unusual fatigue that doesn't improve with rest
- Unexplained mood changes or personality shifts
- Neurological symptoms like dizziness, headaches, or sensory changes
- Symptoms that worsen over time despite self-care efforts
Early intervention often leads to better outcomes. Our neuroinflammation specialist can help determine if inflammation is affecting your brain health and develop a personalized treatment plan.
Take the First Step Toward Brain Health
Schedule a consultation with our neuroimmunology expert to evaluate your symptoms and create a personalized healing plan.
Frequently Asked Questions About Neuroinflammation
What is neuroinflammation?
Neuroinflammation is inflammation in the brain or spinal cord. It can be triggered by autoimmune diseases, infections, toxins, or chronic immune activation and may cause symptoms like brain fog, fatigue, mood changes, or neurological deficits.
What are common symptoms of neuroinflammation?
Symptoms can include brain fog, fatigue, headaches, memory or concentration problems, mood changes, numbness or tingling, weakness, and sometimes vision or balance issues. Not everyone has all of these symptoms however.
How is neuroinflammation diagnosed?
Diagnosis usually involves a detailed history and exam plus tests such as MRI, blood work, and sometimes spinal fluid analysis. Your neurologist pieces these together to see whether inflammation is present and what`s causing it.
What conditions can cause neuroinflammation?
Causes include autoimmune diseases like multiple sclerosis, infections, paraneoplastic syndromes, toxic or metabolic issues, and sometimes long-standing systemic inflammation. Occasionally, no clear trigger is found.
How is neuroinflammation treated?
Treatment depends on the cause and may include immune-modulating medications, steroids, targeted disease-modifying therapies, and lifestyle measures. The goal is to calm the immune system while protecting brain and nerve function.
Can lifestyle changes help reduce neuroinflammation?
Healthy sleep, regular movement, stress reduction, avoiding smoking, and managing conditions like high blood pressure or diabetes can support brain health. These don`t replace medical treatment but they often help the overall picture.
When should I see a neurologist for possible neuroinflammation?
If you have persistent brain fog, unexplained neurological symptoms, or an MRI report mentioning inflammation or demyelination, a neurologist should evaluate you.
About the Author
Dr. Achillefs Ntranos MD
Board-Certified Neurologist
Achilles Neurology Clinic
Dr. Achillefs Ntranos MD is a board-certified neurologist and MS specialist known for his thorough evaluations and compassionate approach. Originally from Greece, he trained at Johns Hopkins University and Mount Sinai Hospital before founding Achilles Neurology Clinic in Beverly Hills to deliver comprehensive, patient-centered neurological care. He specializes in MS, autoimmune neurology, neuropathy, headaches, and other neurological disorders, blending research-driven insights with personalized treatment plans.