Conditions
Expert Neurologist's Guide to White Matter Lesions on Brain MRI
Published: September 14, 2024
Author: Dr. Achillefs Ntranos MD
Do White Matter Lesions Mean You Have Multiple Sclerosis or Dementia?
You just got your brain MRI results back, and they mention "white matter lesions" or "white spots", but your primary doctor's response left you with more questions than answers. What now?
If you're worried these findings suggest multiple sclerosis (MS) or dementia, you're not alone. Understanding what these findings mean for your specific situation is crucial.
The good news: Most white matter lesions are not due to MS or dementia, though some are — here's how to know the difference and what to do next.
What Is White Matter, and How Is It Different from Gray Matter?
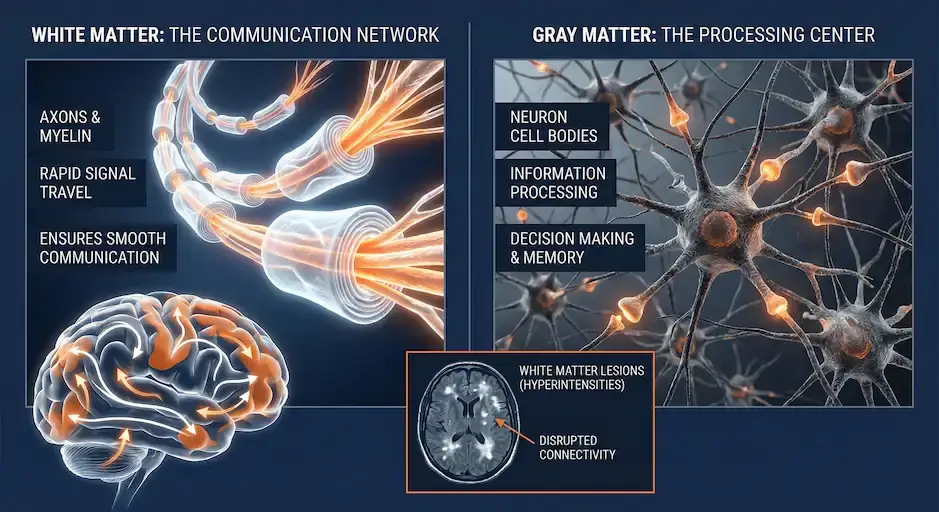
Before we dive deeper into white matter lesions, let's first clarify what white matter and gray matter actually are. Your brain is made up of two primary types of tissue — each with its own distinct yet interconnected role:
White Matter: The Brain's Communication Network
Made up of nerve fibers, called axons, and supporting cells
Covered by a fatty substance called myelin, which gives it a white color
Acts like insulated electrical wires, helping signals travel rapidly between different parts of the brain
Ensures smooth communication and coordination between regions of gray matter
Gray Matter: The Brain's Processing Center
Involved in processing and interpreting information
Called "gray matter" because of its darker color
Consists of neuron cell bodies, dendrites, and synapses (connections between neurons)
Responsible for processing sensory information, decision-making, emotional regulation, memory, and muscle control.
What Are White Matter Lesions?
White matter lesions, also called white matter hyperintensities, refer to areas in the brain where the white matter tissue has experienced damage or changes. These appear as bright or white spots on MRI scans. They signal that something has disrupted normal brain connectivity or blood flow.
While they can sound alarming, these lesions vary greatly in significance, depending on their size, location, and underlying cause.
What Causes White Matter Lesions In The Brain?
White matter lesions can result from a wide range of issues—some relatively benign and others potentially more serious. Common causes include:
Vascular Causes (related to blood vessels):
Aging: Normal aging can cause gradual wear-and-tear on small blood vessels, resulting in lesions.
High Blood Pressure: Chronic hypertension damages the tiny arteries supplying your brain.
Diabetes and High Cholesterol: These conditions affect blood vessels, leading to reduced blood flow and oxygen delivery.
Small Vessel Disease: A common cause where small blood vessels become damaged due to age or cardiovascular risks.
Smoking: Smoking can damage the blood vessels and lead to white matter lesions.
Non-Vascular Causes (not directly related to blood vessels):
Multiple Sclerosis (MS):: Inflammatory diseases like MS can also lead to the formation of white matter lesions as a result of damage to the myelin sheath surrounding brain cells.
Demyelinating Disorders: Conditions that cause the loss of myelin, such as neuromyelitis optica or MOG disease, can result in white matter abnormalities.
Migraines: Chronic migraines can sometimes be associated with subtle white matter changes.
Infections: Certain viral infections (like HIV or Lyme disease) can affect white matter.
Toxic Substances: Chronic alcohol abuse, drug use (e.g., cocaine), or exposure to certain toxins can damage white matter.
Metabolic Issues: Deficiencies in nutrients like Vitamin B12 can lead to white matter abnormalities.
Genetic Conditions (Leukodystrophies): Rare inherited disorders affecting myelin formation.
Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI): A severe impact to the head can cause white matter lesions.
Tumors: Benign or malignant tumors can cause white matter lesions.
Hematological Disorders: Conditions like leukemia or lymphoma can lead to white matter changes.
Autoimmune Disorders: Conditions like lupus or rheumatoid arthritis can cause white matter lesions.
Depending on the type of underlying condition, white matter lesions may progress slowly or rapidly.
Hidden Risk Factors You Should Know
Smoking, poor diet and physical inactivity significantly increases your risk of white matter lesions. These lifestyle factors damage small blood vessels in your brain over time, creating a cumulative effect that accelerates brain aging.
Types of White Matter Lesions
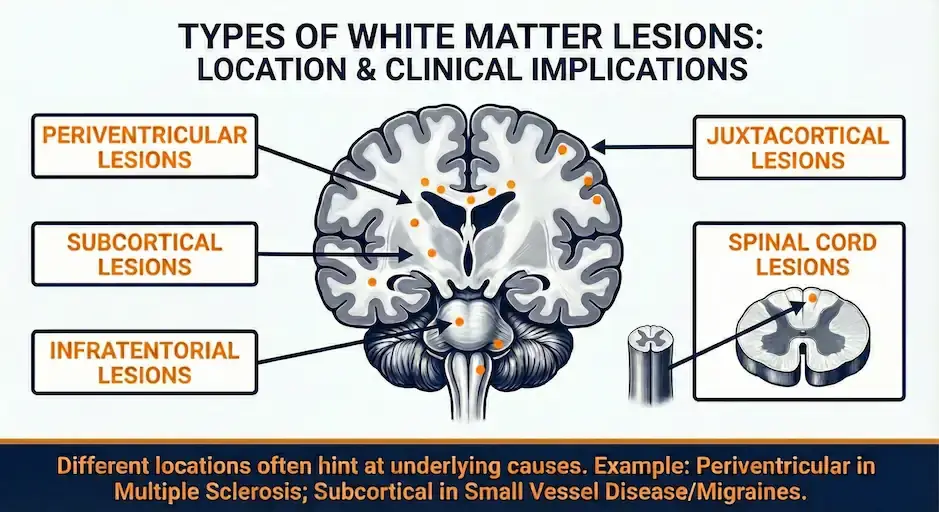
Depending on the type and location, white matter lesions can be classified into different categories:
- Periventricular white matter lesions: Located around the ventricles (fluid-filled spaces) of the brain
- Juxtacortical white matter lesions: Situated at or just below the brain's outer layer (cortex)
- Subcortical white matter lesions: Found in the central regions of white matter, in between the cortex and the ventricles
- Infratentorial white matter lesions: These are located in the lower back part of the brain, such as the brainstem and cerebellum
- Spinal cord lesions: The white matter in the spinal cord can also be affected by certain conditions and form lesions on MRI scans
Different lesion locations often hint at different underlying causes. For example, periventricular lesions are more common in multiple sclerosis, while subcortical lesions are more common in small vessel disease or migraines. Understanding these patterns is crucial for accurate diagnosis, as many conditions can mimic MS on MRI.
Symptoms Associated with White Matter Lesions
Many individuals with white matter lesions might have no noticeable symptoms. However, depending on the severity and location, possible symptoms can include:
- Memory problems
- Difficulty with balance and coordination
- Slower cognitive processing
- Mood changes, including depression or irritability
- Urinary urgency or incontinence (in severe cases)
- Vision changes or dizziness (especially in inflammatory conditions)
These symptoms can vary widely based on the cause and severity of the underlying issue.
How Are White Matter Lesions Diagnosed?
The primary method for diagnosing white matter lesions is through neurological evaluation and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). This non-invasive imaging technique provides detailed pictures of the brain and spinal cord, allowing neurologists to identify and assess white matter changes.
To diagnose white matter lesions, a neurologist usually reviews your MRI images to assess:
- Size, number, and exact location of lesions
- Patterns that help distinguish between potential causes
- Changes over time through follow-up imaging
Additional tests, such as blood work, cognitive testing, spinal fluid analysis, or genetic testing, might be performed to identify specific underlying causes.
What Your MRI Actually Reveals
Your MRI doesn't just show "spots" - it provides critical information about lesion size, location, and pattern that helps distinguish between multiple sclerosis, vascular disease, migraines, and other conditions. Neurologists use the updated 2024 McDonald criteria to diagnose MS, which relies heavily on specific MRI patterns. This precise mapping guides your diagnosis and treatment strategy.
Treatment Options for White Matter Lesions
Managing white matter lesions involves addressing underlying causes and risk factors. Treatment strategies typically include:
Managing Vascular Risk Factors
Since white matter lesions are often linked to vascular health, managing cardiovascular risk factors is a critical part of treatment. Here are some strategies that can help:
- Blood Pressure Control: Medications and lifestyle changes to lower blood pressure are key in preventing further brain tissue damage.
- Cholesterol Management: Statins and other medications, along with dietary changes, can help reduce the risk of white matter lesions.
- Blood Sugar Management: Keeping blood sugar levels in check if you have diabetes can slow the development of these lesions.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Regular exercise, a balanced diet, and avoiding smoking can all help protect your brain health.
Disease-specific Treatments
- Multiple Sclerosis and inflammatory disorders: Steroids, immunotherapies, or disease-modifying drugs.
- Migraine Management: Preventive medications and lifestyle adjustments.
- Vitamin deficiencies: Nutritional supplementation (e.g., Vitamin B12).
Physical Therapy and Cognitive Support
For patients experiencing motor or cognitive symptoms, physical therapy may help improve balance and coordination. Occupational therapy can also help individuals adapt to daily tasks and maintain independence.
If cognitive symptoms such as memory loss or slowed thinking are present, neuropsychological-testing and cognitive rehabilitation strategies can help improve brain function.
Beyond Medication: Keys to Brain Protection
While medications target specific conditions, research shows that combining them with lifestyle changes can improve their effectiveness. Quitting smoking, Mediterranean diet adoption, and just 150 minutes of weekly exercise can have a significant impact on your brain health.
When to See a Neurologist for White Matter Lesions
If you've been diagnosed with white matter lesions or are experiencing symptoms that concern you, it's essential to consult with a neurologist. A comprehensive multiple sclerosis evaluation can provide a thorough assessment, interpret your MRI results in context, and develop a personalized treatment plan.
Expert Specialized Care Makes the Difference
Our board-certified neurologist specializes in diagnosing and managing conditions related to white matter lesions and is able to distinguish between similar-appearing but different causes of white matter lesions. This ensures you receive the most appropriate and personalized treatment.
Living with White Matter Lesions
For many people, white matter lesions don't significantly impact daily life. However, proactive care can make a big difference:
- Follow your neurologist's recommendations closely.
- Maintain regular follow-up visits to track your brain health.
- Report new or worsening symptoms promptly.
- Adopt a healthy, active lifestyle to protect your brain.
White Matter Lesions and Flying
Pilots with white matter lesions on brain MRI may require an FAA neurological evaluation for medical certification. We provide comprehensive evaluations and documentation for pilots with neurological findings.
White Matter Lesions and Driving
Patients with white matter lesions may need a DMV driver evaluation to maintain their driving privileges. We provide comprehensive evaluations and documentation for patients with neurological findings.
Conclusion
White matter lesions are a complex topic, but understanding them is an important step in managing your brain health. While they can be concerning, many people with white matter lesions lead normal, healthy lives. By working closely with our expert neurologist and focusing on overall health, you can take proactive steps to support your brain function and well-being.
If you have questions about white matter lesions or would like to schedule a consultation, our multiple sclerosis clinic in Los Angeles offers expert evaluation and care. Your brain health is our priority, and we're here to provide the specialized support you need.
Ready To Take The Next Step?
Connect with our white matter expert and elevate your neurological health today.
Frequently Asked Questions About White Matter Lesions
What are white matter lesions on a brain MRI?
White matter lesions are small areas of change in the brain's wiring seen on MRI. They are very common, especially with age, migraines, and vascular risk factors, and they don't always mean a serious disease.
Do white matter lesions mean I have multiple sclerosis (MS)?
Not necessarily. Some patterns of white matter lesions are typical for MS, but many others are due to aging, migraines, small vessel disease, or other causes. A neurologist looks at the lesion pattern, your symptoms, and your exam before diagnosing MS.
Can white spots on a brain MRI be harmless?
Yes. Many people have harmless white spots related to age, blood pressure, or migraines and never develop MS or dementia. Your neurologist can tell you whether your specific MRI findings are concerning.
What causes white matter lesions in the brain?
Common causes include chronic small vessel changes (often from high blood pressure or diabetes), migraines, prior mild injuries or infections, and, less commonly, inflammatory diseases like MS. Sometimes no single cause is found.
Do white matter lesions go away or heal over time?
Some lesions can shrink or become less active, while others remain as "scars" on MRI even if you feel well. Follow-up imaging helps your neurologist see whether there are new lesions or changes over time.
When should I see a neurologist for white matter lesions?
You should see a neurologist if your MRI report mentions white matter lesions and you have symptoms like vision changes, numbness, weakness, balance problems, or cognitive changes, or if you are worried the lesions might mean MS.
About the Author
Dr. Achillefs Ntranos MD
Board-Certified Neurologist
Achilles Neurology Clinic
Dr. Achillefs Ntranos MD is a board-certified neurologist and MS specialist known for his thorough evaluations and compassionate approach. Originally from Greece, he trained at Johns Hopkins University and Mount Sinai Hospital before founding Achilles Neurology Clinic in Beverly Hills to deliver comprehensive, patient-centered neurological care. He specializes in MS, autoimmune neurology, neuropathy, headaches, and other neurological disorders, blending research-driven insights with personalized treatment plans.